In this write-up, I’ll utilize the ELK stack knowledge I obtained from the previous room to investigate a potential malware infection. By going through a mock incident, utilizing real-world data sources such as proxy logs, I will gain hands-on practice in core techniques like event correlation, pivoting to an an IP address to find other systems that have communicated with it, and open-source intel gathering.
Room link: Itsybitysy
Task 1: Introduction
In this challenge room, we will take a simple challenge to investigate an alert by IDS regarding a potential C2 communication.
Room Machine
Before moving forward, deploy the machine. When you deploy the machine, it will be assigned an IP Machine IP: MACHINE_IP. The machine will take up to 3-5 minutes to start. Use the following credentials to log in and access the logs in the Discover tab.
Username: Admin
Password: elastic123
Answer the questions below
Connect with the lab
Task 2: Scenario – Investigate a potential C2 communication alert
Scenario
During normal SOC monitoring, Analyst John observed an alert on an IDS solution indicating a potential C2 communication from a user Browne from the HR department. A suspicious file was accessed containing a malicious pattern THM:{ ________ }. A week-long HTTP connection logs have been pulled to investigate. Due to limited resources, only the connection logs could be pulled out and are ingested into the connection_logs index in Kibana.
Our task in this room will be to examine the network connection logs of this user, find the link and the content of the file, and answer the questions.
Answer the questions below
How many events were returned for the month of March 2022?
Answer: 1482
Filter events only for the month of March
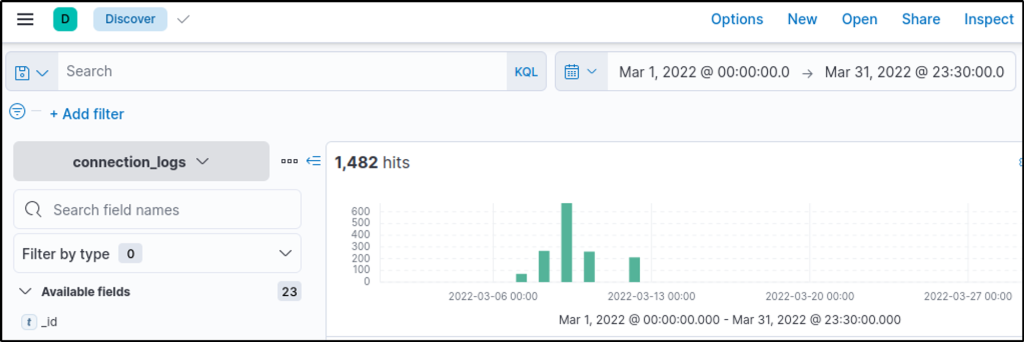
What is the IP associated with the suspected user in the logs?
Answer: 192.166.65.54
The first IP address is very tempting to be considered a malicious IP address because of its sheer number of events. But further analysis would say otherwise.
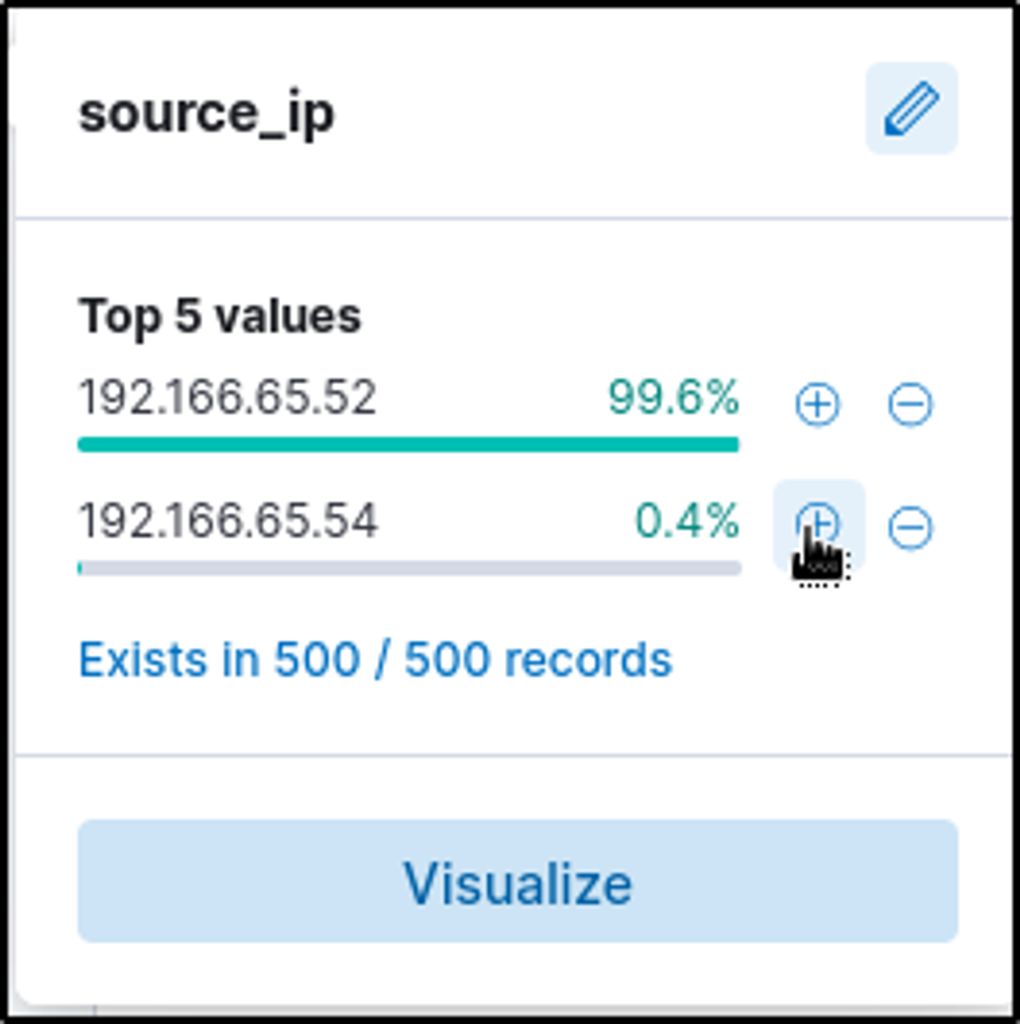
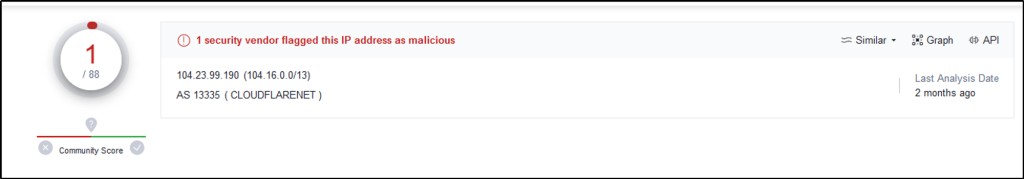
Selecting the second source_ip value, two events were filtered. It shows that this IP address is communicating to an external IP address with “104.23.99.198”.
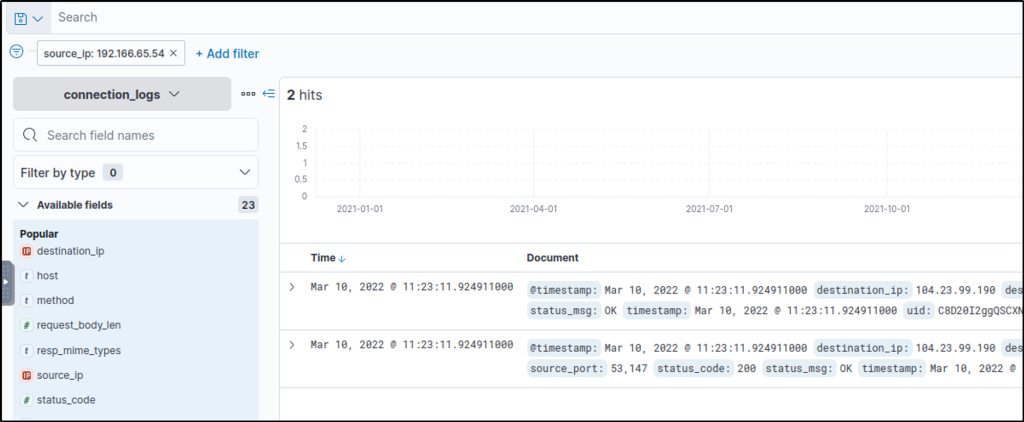
Upon further investigation using Hybrid Analysis and VirusTotal, the IP address is found to be malicious.
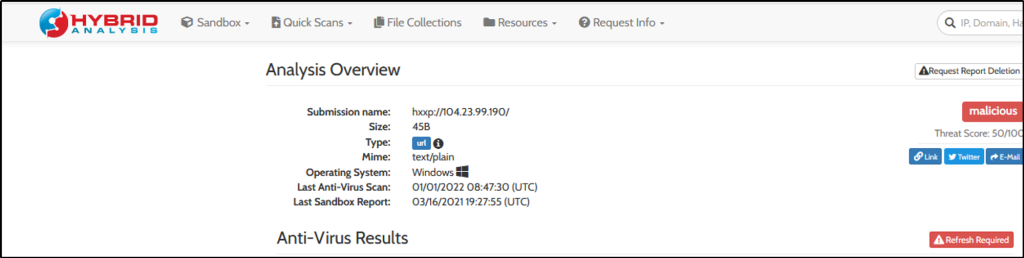
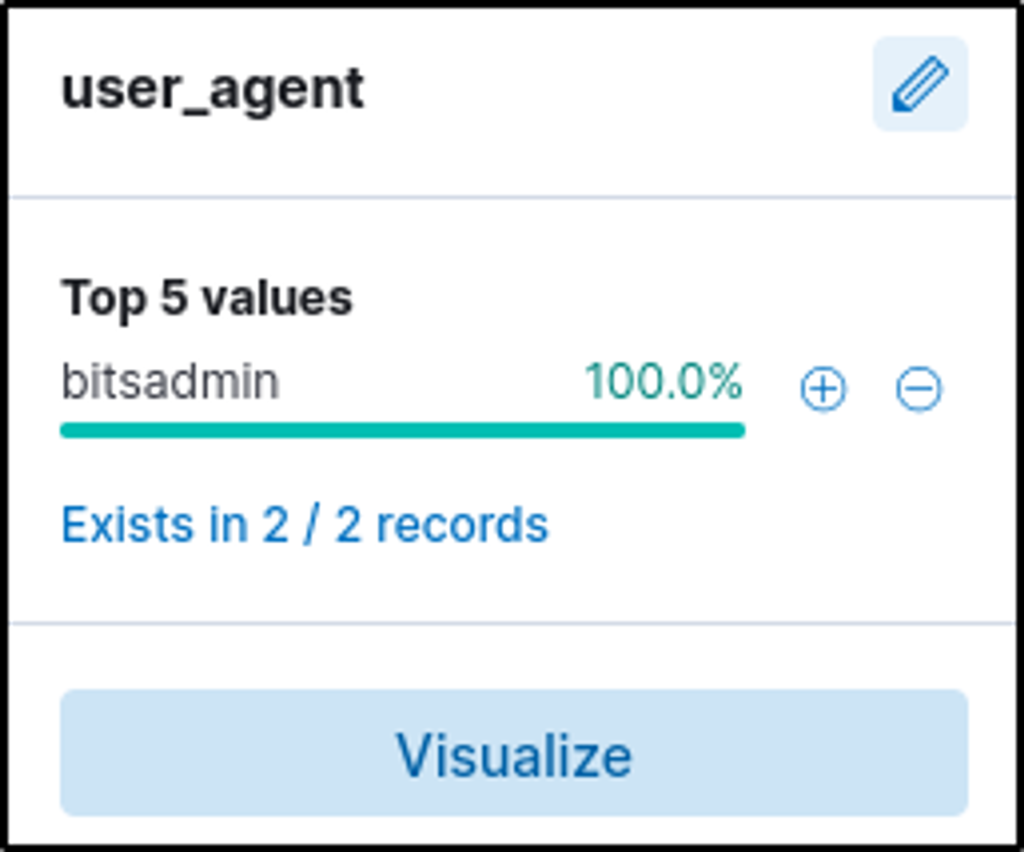
The user’s machine used a legit windows binary to download a file from the C2 server. What is the name of the binary?
Answer: bitsadmin
On the left panel, the “user_agent” field name is where the name of the tool used to download a file would be found.
BITSAdmin is “a command-line tool that you can use to create download or upload jobs and monitor their progress”.
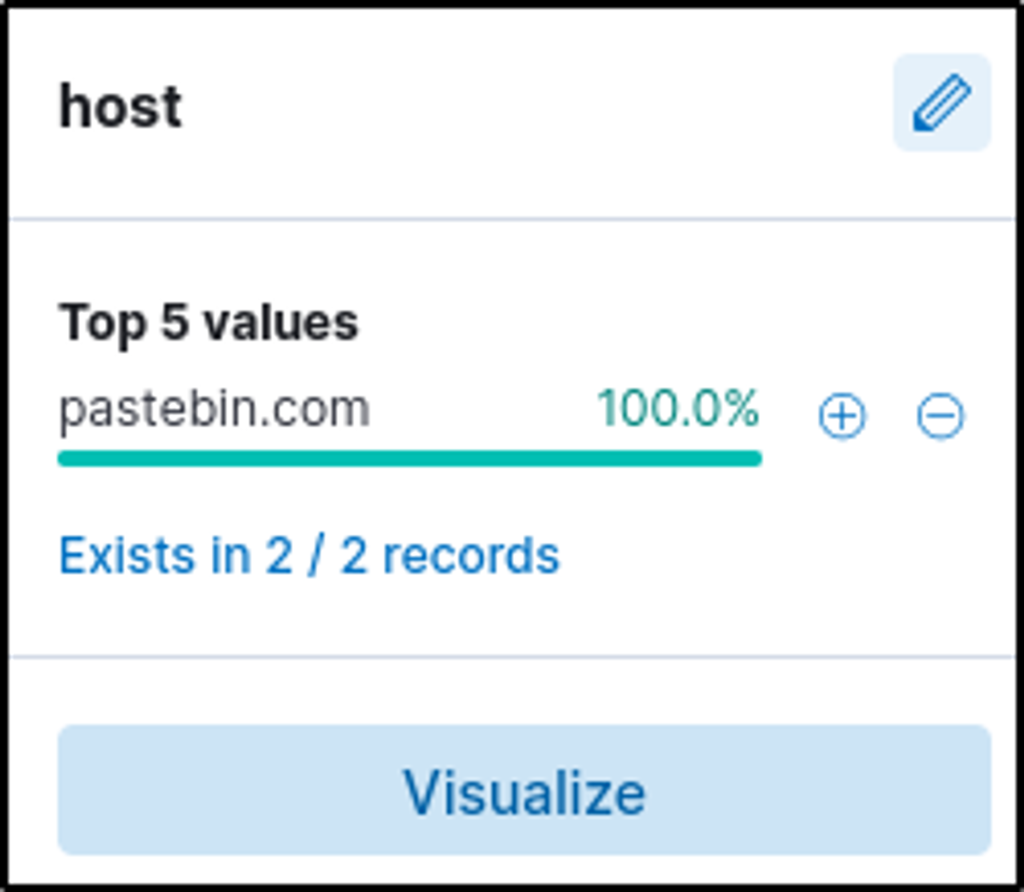
The infected machine connected with a famous filesharing site in this period, which also acts as a C2 server used by the malware authors to communicate. What is the name of the filesharing site?
Answer: pastebin.com
Click on the “host” field.
What is the full URL of the C2 to which the infected host is connected?
pastebin.com/yTg0Ah6a
“URI” field contains the URI value. The full URL would consist of the server name and the identified URI.
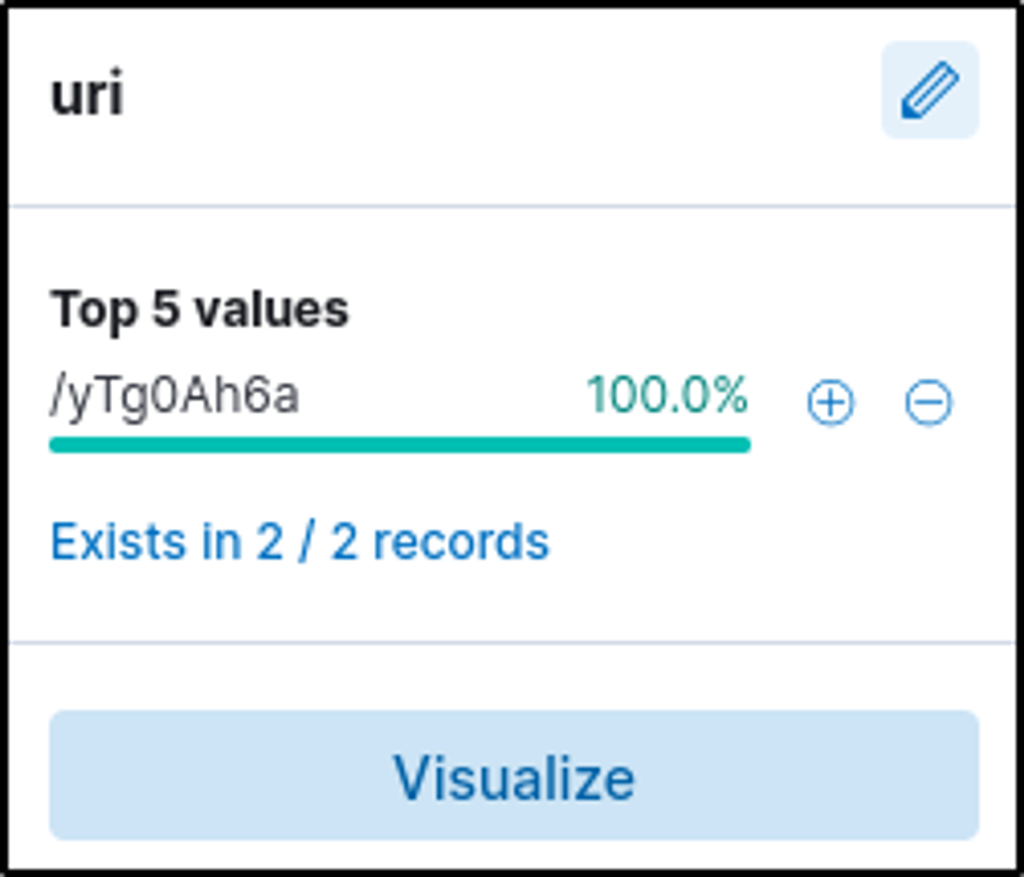
A file was accessed on the filesharing site. What is the name of the file accessed?
Answer: secret.txt
Open a website and navigate to the URL of the C2. It should contain the name of the file and its content.
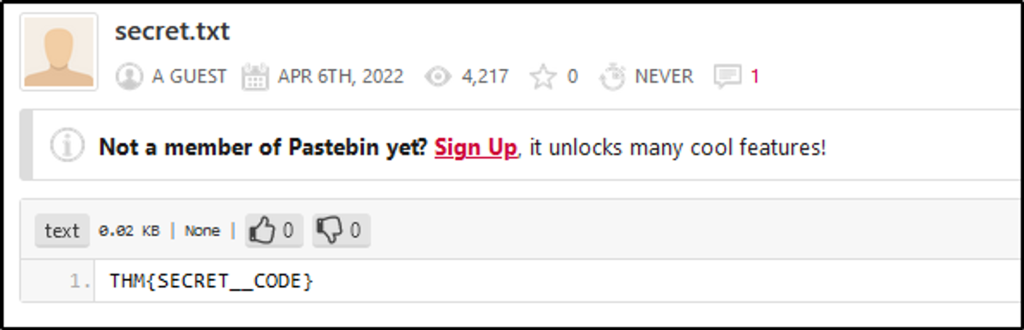
The file contains a secret code with the format THM{_____}.
Answer: THM{SECRET__CODE}
I acquired practical experience in threat hunting through this authentic exercise conducted in Kibana. This exercise involved utilizing log analysis to detect and investigate security incidents. The skills I honed, such as examining data points and examining proxy logs, are directly applicable to real-life threat hunting scenarios.
Thank you for reading. Until next time 🙂


Leave a comment